In the world of surgery, there are many surgical methods that are used to treat different types of ailments. Among them, laparoscopic and laser surgery methods are the most prominent. Both surgeries are minimally invasive and do not involve making large incisions like open surgeries. Both have different purposes and help treat different sorts of health issues. In this article, we’ll look closely into both treatments and learn about their purpose, advantages, complications, etc. What are the main differences between laparoscopy and laser surgery? > Laparoscopic surgery involves small incisions on the body, using a laparoscope and small instruments to operate internally. > Laser surgery uses a focused beam of light energy to cut, vaporize, or seal tissue, without necessarily needing incisions, and it can target tissues with precision. Both laparoscopy and laser surgeries are minimally invasive surgeries. However, they differ in the way the surgeries are performed. The table below will help you understand some of the main differences between laparoscopy and laser surgery. Laparoscopic surgery Laser surgery Involves making small incisions (about 0.5–1 cm) on your body Can be performed with or without incisions depending on the procedure A laparoscope and other small instruments are inserted through the incisions to view and operate the inside of your body Uses a focused beam of light energy to cut, vaporize, or seal tissue The surgeon uses the Laparoscopic instruments to manipulate and repair tissues like suturing or tying knots The surgeon uses a light beam to target tissues and operate on them Relies on a camera inserted in a tube (laparoscope) to guide the instruments and perform the surgery It can be performed under direct vision or even use cameras or specialized imaging depending on the type of surgery Is laparoscopy and laser surgery same Laparoscopy and laser surgery are not the same, though they can be used together. Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that involves making small incisions to insert a camera and instruments for diagnosis or treatment. Laser surgery, on the other hand, uses focused light beams to cut or destroy tissue and can be performed through laparoscopic techniques. While laparoscopy can utilize lasers for specific procedures, they represent different approaches to surgery. Understanding the laparoscopic surgery A few years ago, if you wished to undergo surgery, even if it was minor, your doctor had to make a large incision near the surgery site. There are a few types of incisions are there in Laparoscopy such as Single Incision Your muscles will be opened and stitched back together after the surgery. Laparoscopic surgery—also called a keyhole surgery—is an alternative to this method. It is a minimally invasive procedure that involves making small incisions near the incision site and inserting surgical instruments to perform the surgery. Your surgeon will be holding the surgical instruments and operating your tissues and organs with the help of a laparoscope (a thin rod with a camera at the end) to view your insides. Understanding the Laser surgeries Laser treatments are surgical procedures that are performed using focused light. Laser is short for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.” This light has a specific wavelength that allows doctors to focus on a certain body part and work on it. You might experience less pain, scarring, or swelling with laser surgeries. What surgeries are performed laparoscopically? Laparoscopy is commonly used for abdominal and pelvic issues, including hernia repair and infertility problems. A laparoscopy is mainly performed to treat issues in the abdominal and pelvic areas. It can either be done for diagnostic purposes (to diagnose issues that imaging tests can’t identify) or to perform surgeries and correct issues like removing unwanted growths, removing blockages, etc. Laparoscopies are majorly performed in hernia repair and correcting issues that cause infertility, like fallopian tube blockages, endometriosis, fibroids, etc. Some surgeries that can be performed laparoscopically are Biopsies, Small tumor removals, Ectopic pregnancy removal, Cholecystectomy, Urethral and vaginal reconstruction surgery, Appendectomy, etc. When do surgeons use Laser surgeries? Laser surgeries are utilized in various fields like ophthalmology, dentistry, dermatology, and cancer treatments for specific conditions like kidney stones removal or vision improvement. Laser surgeries are used in various fields depending on their needs. It is more commonly used in fields like ophthalmology (LASIK), dentistry (gum reshaping), dermatology (skin resurfacing), and cancer treatments. Laser therapies are prominently used to treat the following conditions. To remove kidney stones To shrink or destroy polyps, tumors, or precancerous growths To repair a detached retina To remove part of the prostate To improve vision To treat pain, including back nerve pain Is Laparoscopy a common surgical method? Yes, laparoscopy is a fairly common surgical method surgeons prefer in cases where open surgery is not required. According to studies, about 13 million laparoscopic surgeries are performed worldwide annually. This number is estimated to grow with the development of technologies and the latest medical innovations. Advantages of laparoscopy and laser surgery Both laparoscopic and laser surgeries are minimally invasive, leading to shorter recovery times, less pain, lower infection risks, and minimal scarring. Below are some advantages of choosing a laparoscopic and laser surgery method for your surgery Advantages of Laparoscopic surgery Advantages of Laser surgery Minimally invasive surgery Minimally invasive surgery Only small incisions are needed to conduct the surgery Can be performed with or without incisions depending on the procedure Shorter recovery time Shorter recovery time Less pain after surgery Less pain after surgery Lower risk of bleeding or infections during and after surgery Lower risk of bleeding or infections during and after surgery Shorter hospital stay. You can resume your daily activities after a few days Shorter hospital stay. You can resume your daily activities after a few days Minimal scarring Minimal scarring Complications of laparoscopy and laser surgery Below are some complications that may arise from a laparoscopic and laser surgery method. Complications of Laparoscopic surgery Complications of Laser surgery More expensive than open surgery More expensive Risk of injury to the blood vessels, bowel, and nerves Can sometimes cause side effects like bleeding,
Single Incision Laparoscopic surgery
Previously, before laparoscopy was invented, surgeons used to perform open surgeries, where a single long incision was made to open your body and operate on it. Then, to prevent risks of infections and improve recovery rate, laparoscopy was introduced, where only 3 or 4 tiny incisions were made on your body to correct your issue. Now, technology has advanced, and there is no longer a need to have 3 or 4 incisions on your body. This advancement is called a single incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS), where you only need one incision to conduct a laparoscopic surgery. Read this article till the end to learn more about SILS and how the procedure is performed. What Is A Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS)? A single-incision laparoscopic surgery is an advanced laparoscopic procedure where a single incision is made near the belly button to perform the surgery. The surgical instruments and the laparoscope are inserted through that single incision, and the surgery is conducted. This method was introduced to reduce the need for incisions in patients and reduce their discomfort and recovery time. It also serves cosmetic purposes, as patients don’t need to have too many scars on their bodies. The incision is also made near the belly button, making the scar less noticeable. SILS Vs. Conventional Laparoscopic: Key Difference The below table will show you the major differences between SILS and conventional laparoscopic procedures. SILS Conventional laparoscopy Lowers risk of infection & other complications Has slightly more risk of infection and other complications than SILS Less pain after surgery, and recovery time is shorter Can be a bit painful, and the recovery time is a bit longer than SILS Has cosmetic benefits. Only one incision is made, and that, too, can be hidden within the belly button. Three or four incisions are made around the surgery site. This can scar your abdomen. Lower risk of suffering nerve injury Slightly higher risk of nerve injury due to Laparoscopic surgical instruments. Single-Incision Laparoscopic Surgery Advantages And Disadvantages Advantages SILS is rapidly evolving, and many surgeons are adopting this method of laparoscopy over traditional laparoscopy. SILS is especially useful in effectively treating conditions related to the liver, pancreas, gall bladder, and appendix. It is also helpful in treating patients who need a second surgery or had a relapse. The surgeon only needs to make a slightly longer incision than the previous one. This reduces the risks of adhesions and other complications. It also reduces the risks of injury and pain during and after the surgery. The recovery time is also lower than in open or conventional laparoscopic surgeries. Disdvantages & Limitations SILS has several advantages over laparoscopic surgeries. However, it might not be the best option while treating some patients. For example, SILS is not the best option for tall patients. The SILS instrument will not be long enough to reach the surgery site if it is a bit far from the belly button. The SILS instrument will also not be comfortable to handle if the surgery requires stitching an organ or tissue structure together. The shape of the instrument may not be suitable for this procedure. It is also not suitable if you are treating high-risk patients whose surgical site is close to a major blood vessel. Any injury can harm the vessel and lead to blood loss. These patients might have to undergo open surgery. The Evolution Of Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery Over The Years SILS is an effective laparoscopic procedure that has helped several patients and surgeons conduct less messy and successful surgeries. Now, let’s look at its history and how it came about to be used in several surgical procedures. 1. SILS was first introduced in 1969 in the field of gynecology, where about 4000 tubal ligations were performed through small incisions near the belly button. The SILS procedure was highly successful and was then used in several elective female sterilization procedures. 2. In 1992, this technique was used to conduct successful appendectomies without complications in 25 patients. 3. In 1997, SILS was used to perform cholecystectomy in around 30 patients, and it was a success. Following this, SILS has been increasingly used to perform several general surgeries with minimal complications. The cosmetic benefit of the procedure is an added bonus for several patients who wish to reduce scarring and post-surgical pain. Conclusion Single-incision laparoscopic surgeries have become an effective alternative for patients who wish to have a scarless surgery. However, remember that this procedure is not suitable for all cases. Some procedures might require an open or conventional laparoscopy. Ensure you discuss it with your laparoscopic surgeon and understand what procedure suits your condition. Choose the procedure that can treat your issue and minimize the chances of recurrence. Contact Form Demo NameEmailYour MessageSubmit Dr. K. Amilthan MBBS., MS., FMAS., FALS. Heal Your Hernia Now: 20+ Years of Experience 1,000+ Surgeries Your Journey to Wellness Begins with us. Book Appointment Edit Template Dr. Amilthan Dr. Amilthan is a renowned laparoscopic hernia surgeon based in Chennai, with over 20 years of experience in general surgery. He completed his MBBS and MS in General Surgery at Kilpauk Medical College and Government Royapettah Hospital in Chennai. Edit Template All Posts Hernia Blog Single Incision Laparoscopic surgery Previously, before laparoscopy was invented, surgeons used to perform open surgeries, where a single long incision was made to open… Read More Difference between Laparoscopy and Laparotomy Laparoscopy and laparotomy are common surgical procedures. They help perform surgeries in the abdominal and pelvic region. The primary difference… Read More Difference between Laparoscopy and Endoscopy Laparoscopy and endoscopy are minimally invasive medical procedures. Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure. Endoscopy is a diagnostic procedure. Both procedures… Read More Load More End of Content.
Difference between Laparoscopy and Laparotomy
Laparoscopy and laparotomy are common surgical procedures. They help perform surgeries in the abdominal and pelvic region. The primary difference between laparoscopy and laparotomy is the size of the incision. “Laparo” means “Wall of the abdomen” in Ancient Greek. Further, the use of laparoscopy and laparotomy differs from ailment to ailment. The key differences between laparoscopy and laparotomy are many. The following section explains the differences. What are the Key Differences Between Laparoscopy and Laparotomy? The primary difference is the type of incision laparoscopy and laparotomy make. There are certain types of incisions in Laparoscopy such as Single incision Laparoscopy is often called “Keyhole Surgery” as it makes only a small incision. Surgeons view the insides of the body and operate through this cavity. Laparotomy cuts open the wall of the abdomen to perform surgery.Laparoscopy is usually used for biopsy. Laparotomy aids in lithotomy, appendectomy, and other organ removal. Laparotomy is also undertaken to remove pelvic organs in women.The time taken to recover, rate of infection, and degree of pain are lesser for laparoscopic surgery than for laparotomy. Understanding the Laparoscopic Surgery Laparoscopic surgery is also called “minimally invasive surgery”. It makes smaller incisions on the needed area of the abdomen to operate. Biopsy and minor surgeries such as cyst removal, and appendix removal use laparoscopy. Laparoscopy is a recent development in medical procedures. The instruments used in laparoscopy are expensive and demand high expertise. Understanding the Laparotomy Surgery Laparotomy is also called “celiotomy”. The surgery makes a large incision on the abdominal wall. It cuts through tissues and fascia to gain access to organs in the abdominal and pelvic region. A sagittal midline incision is the standard incision made during laparotomy.A paramedian is a vertical incision. This incision cuts one side of the sagittal plane for better access to the kidneys and adrenal glands. A transverse incision is a horizontal incision made below the navel. A pfannenstial incision makes cuts above the pubic bones for pelvic laparotomy. A subcostal incision or Kocher incision is a diagonal incision. It helps to operate on organs such as the spleen, liver, bile duct, etc.A chevron or rooftop incision is also a subcostal incision. It makes an incision on either side of the midline. It permits access to kidneys and organs in the middle region. What Surgeries are Performed Laparoscopically? Surgeries that use laparoscopy include: Cholecystectomy Appendectomy Lithotomy Endometriosis Ovaries removal Ovarian cysts removal Adhesion removal etc. When do Surgeons Choose Laparotomy? Medical practitioners have administered laparotomy for ages. Laparotomy is the go-to surgical procedure during most of the emergencies.Surgeons also choose laparotomy for the removal of organs in the peritoneal cavity. Is Laparoscopy a Common Surgical Method? Yes, laparoscopy is a common surgical method nowadays. Surgeons suggest laparoscopy to diagnose any disease condition or for biopsies. It is an alternative to cutting open through the abdomen. Minor surgeries can employ laparoscopy. How Common is Laparotomy? C-section is normally carried out through laparotomy. Laparotomy is also used to identify cancer stage and is called “Staging Laparotomy.” Advantages The advantages of laparoscopy and laparotomy are many and vary. The choice of surgery though depends upon the condition of the disease and the treatment proposed. What are the Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery? For minor surgeries and biopsies, a laparoscopic surgery would be helpful. The smaller incisions made in laparoscopic surgery heal quicker and leave no scar. The recovery rate post-surgery is also faster when compared to laparotomy. Since the abdominal wall is not cut open the infection rate is negligible and the pain bearable. What are the Advantages of Laparotomy Surgery? Laparotomy gives a shorter learning curve for surgeons making it easier and quicker to diagnose and treat diseases. The mobility range of medical instruments in laparotomy is also higher. Laparotomy has less chance for cancer spoilage as well due to wider mobility. Complications Alongside its benefits, both laparoscopy and laparotomy have its side-effects as well. Though the choice of surgery is based upon the degree of emergency and ailment condition it is advisable to be aware of the complications both these surgeries entail. What are the Complications of Laparoscopic Surgery? Laparoscopic surgery is dependent on the image transmitted by the camera set on the laparoscope.Surgeons have limited mobility through the keyhole incision and there is an unfortunate possibility of cancer spillage to other body parts and planes. What are the Complications of Laparotomy Surgery? The large incision made by laparotomy can leave surgical scars on the abdomen. The rate of infection in laparoscopic surgery is also higher as it opens up the abdominal wall. Patients also will suffer quite some pain post laparotomy. Recovery Time The rate of recovery differs from laparoscopy to laparotomy. The recovery time for laparotomy is higher than the recovery time for laparoscopy. What is the Recovery Time for Laparoscopic Surgery? Laparoscopy does not need hospitalization for more than a day. Within a week patients can carry out their normal activities. The incision scars also heal faster. What is the Recovery Time for Laparotomy Surgery? Laparotomy requires at least six weeks of hospitalization. Internal bleeding and possible infection demand long hospitalization. The recovery period would vary from the kind of laparotomy employed. It takes into account other related procedures undertaken as well.Patients would have to consult their doctor before discharge. They may have to take precautionary steps for quite some time post-laparotomy. Conclusion The primary difference between a laparoscopy and a laparotomy is the length of incisions. Laparoscopy is a recent development with the need for expensive instruments. Laparotomy is a widely used procedure. The choice of surgery though depends upon the nature and degree of ailment and urgency.To know more about the details of laparoscopy and laparotomy contact a surgeon. Contact Form Demo NameEmailYour MessageSubmit Dr. K. Amilthan MBBS., MS., FMAS., FALS. Heal Your Hernia Now: 20+ Years of Experience 1,000+ Surgeries Your Journey to Wellness Begins with us. Book Appointment Edit Template Dr. Amilthan Dr. Amilthan is a renowned laparoscopic hernia surgeon based in Chennai, with over 20 years of experience in
Difference between Laparoscopy and Endoscopy
Laparoscopy and endoscopy are minimally invasive medical procedures. Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure. Endoscopy is a diagnostic procedure. Both procedures use thin tube-like structures with a camera attached to them. It is used to view the insides of the body. Laparoscopy uses a laparoscope to view the insides of the abdomen and pelvic region. Endoscopy uses an endoscope to view the digestive tract What are the Key Differences Between Laparoscopy and Endoscopy? Laparoscopy operates on the abdominal and pelvic region. It uses a laparoscope. It is an instrument to view the body’s insides. Small incisions made on the abdomen enable the laparoscope to go through the abdominal wall. Endoscopy views the digestive tract to diagnose it. The endoscope needs no incisions. It uses the oral or anal orifices to enter into the body. Understanding the Laparoscopic Surgery Laparoscopy helps in hysterectomy, appendix removal, and other minor surgeries. Laparoscopy is chiefly meant to treat ailments in the abdominal and pelvic regions. Laparoscopy causes less post-surgery pain. It requires less recovery time as well. Laparoscopy uses expensive instruments to carry out the procedure. Understanding Endoscopy Endoscopy diagnoses disease in the esophagus and stomach areas. It makes no incisions on the patient’s body. The endoscope travels through the digestive tract to identify diseases. It can also collect tissue samples for biopsy. Local anesthesia is enough to undertake this procedure. What Surgeries are Performed Laparoscopically? Surgeries that use laparoscopy include: Cholecystectomy Appendectomy Lithotomy Endometriosis Nephrectomy Ovaries removal Ovarian cysts removal Adhesion removal Adrenalectomy When do Surgeons Choose Endoscopy? Surgeons choose endoscopy for diagnostic purposes of the digestive system. Endoscopy enables a view of the tract before any required surgery. Surgeons can use endoscopy before finalizing the need for surgery. Endoscopy helps in biopsy pre-surgery. Is Laparoscopy a Common Surgical Method? Yes, laparoscopy is a common surgical method. Laparoscopy is gaining popularity over the years as it is minimally invasive. Laparoscopy causes little infection and bleeding. The rate of recovery is also quick. So laparoscopy is widely preferred. How Common is Endoscopy? Endoscopy is a common diagnostic procedure. Endoscopy helps identify any discomfort in the digestive tract and ulcer formations in the stomach. The most commonly performed endoscopy is upper endoscopy. It diagnoses the esophagus, stomach, and a part of the duodenum. Advantages Laparoscopy and endoscopy have enormous benefits regarding diagnosing the body’s insides without large incisions. Also, both laparoscopy and endoscopy ensure the disease is first diagnosed before surgery. What are the Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery? The advantages of laparoscopic surgery include: Faster recovery rate post-surgery Smaller incisions that heal quicker and leave no scar Lesser pain Lesser infection Best for minor surgeries and biopsies in the abdominal region What are the Advantages of Endoscopy? Endoscopy does not make any incisions. So there is no fear of blood loss. Also, there are various endoscopy procedures available. Some include: Anoscopy for disease in the rectum or anus Bronchoscopy for issues in lungs and windpipe Colonoscopy for the colon and large intestine Colposcopy for vagina and cervix Esophagoscopy for esophagus Laryngoscopy for larynx and so on Complications There are complications such as infection, perforation, and so on with laparoscopy and endoscopy. Yet the benefits of laparoscopy and laparotomy outweigh the disadvantages of these surgeries. What are the Complications of Laparoscopic Surgery? The complications of laparoscopic surgery include: Limited mobility for laparoscopic instruments Dependent on the image transmitted by the laparoscope camera Cancer spillage possibility What are the Complications of Endoscopy? The complications of endoscopic surgery include: Perforation of the endoscope instruments Limited mobility Dependent on the image transmitted by the endoscope camera Recovery Time The recovery time of laparoscopy and endoscopy is minimal most of the time. However, the gravity of the laparoscopic surgery will decide on the recovery time. What is the Recovery Time for Laparoscopic Surgery? Patients may leave for home on the very day of laparoscopy surgery. Major surgeries done through laparoscopy may require hospitalization for a few days. During the recovery phase, the patients need to know what to eat and what foods to avoid after the laparoscopic surgery. What is the Recovery Time for Endoscopy? The recovery time for endoscopy is a single day if local anesthesia is administered. Patients may feel discomfort in the areas where the endoscope was inserted. Other than that endoscopy does not require a lengthy recovery time. Conclusion Laparoscopy and endoscopy are two profitable gifts that the advancement of the medical field has provided us with. You can choose laparoscopy if the surgery is a minor one. Doctors recommend endoscopy for diagnosis most of the time. So it is best to consult your surgeon or physician to choose the procedure needed to diagnose or operate on your ailment. To know more about the details of laparoscopy and endoscopy contact a surgeon. Contact Form Demo NameEmailYour MessageSubmit Dr. K. Amilthan MBBS., MS., FMAS., FALS. Heal Your Hernia Now: 20+ Years of Experience 1,000+ Surgeries Your Journey to Wellness Begins with us. Book Appointment Edit Template Dr. Amilthan Dr. Amilthan is a renowned laparoscopic hernia surgeon based in Chennai, with over 20 years of experience in general surgery. He completed his MBBS and MS in General Surgery at Kilpauk Medical College and Government Royapettah Hospital in Chennai. Edit Template All Posts Hernia Blog Difference between Laparoscopy and Endoscopy Laparoscopy and endoscopy are minimally invasive medical procedures. Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure. Endoscopy is a diagnostic procedure. Both procedures… Read More Navel Displacement Symptoms The navel is considered the body’s midpoint, Do you feel pain in your belly button and notice your navel shifting… Read More Difference Between Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are advanced surgical methods that use little to no incisions respectively to carry out surgeries. Laparoscopy is… Read More Load More End of Content.
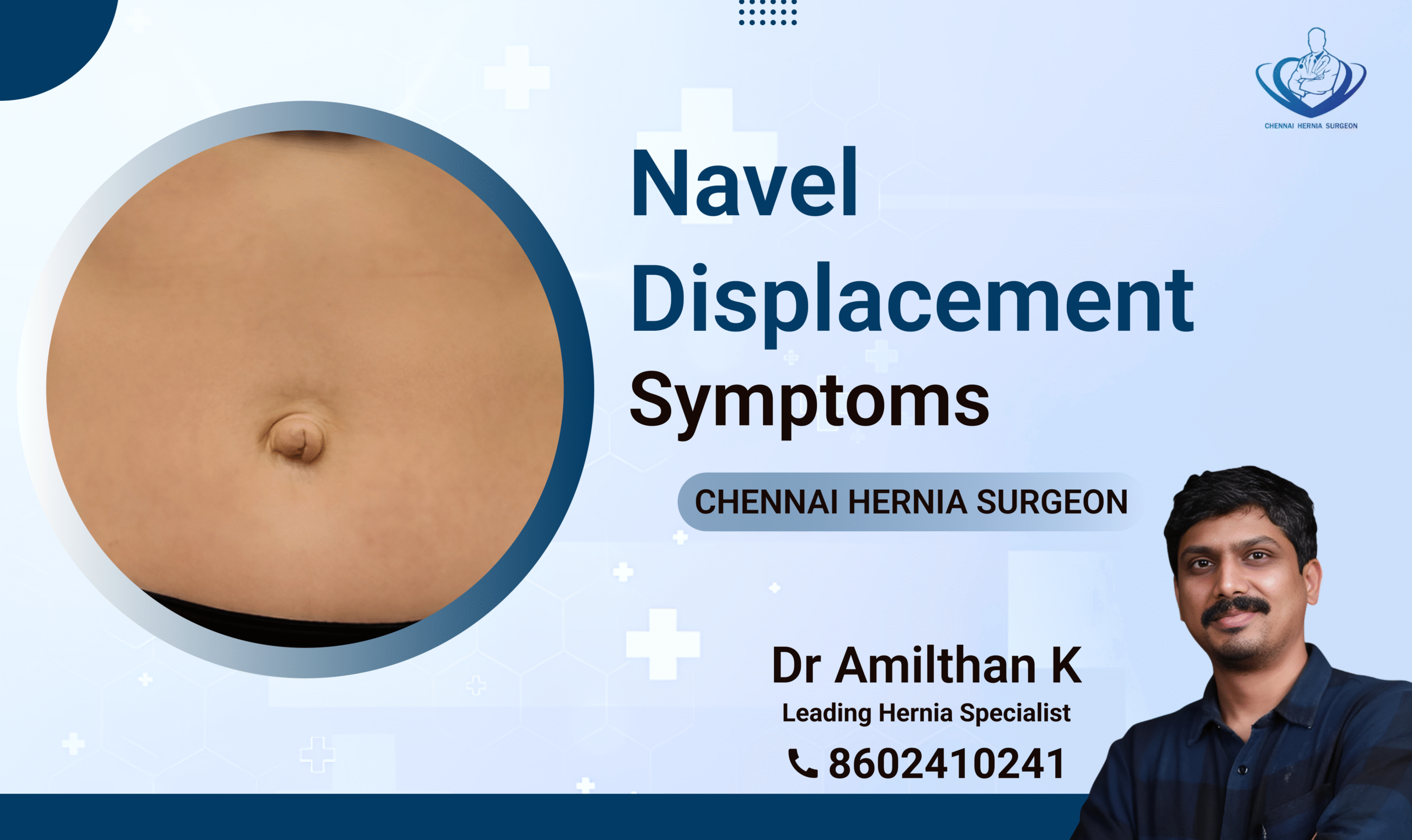
Navel Displacement Symptoms
The navel is considered the body’s midpoint, Do you feel pain in your belly button and notice your navel shifting from its point or protruding in an unusual way? Then, it might be due to navel displacement. In this article, we have discussed in detail what navel displacement is, its symptoms, causes, and some treatment options for the condition. Continue reading the article to know more about the issue. What is navel displacement? Navel displacement is a condition where the belly button is positioned differently, causing discomfort. Navel displacement is also known as a misplaced belly button, This condition in which the navel is positioned differently from the usual location in the anterior abdominal wall. It is almost similar to spinal cord displacement. Here, the navel slips or displaces from the center. It is mostly noticeable while constipating or lifting heavy weights, causing an uncomfortable sensation in the belly button area and unusual protrusion. Navel Displacement Symptoms Symptoms include abdominal pain, digestive issues, back pain, nausea, fatigue, and more. Navel displacement can lead to a range of symptoms affecting various bodily functions. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking appropriate treatment and alleviating discomfort. Navel displacement side effects Naval Displacement Symptoms Description Abdominal Pain Pain around the navel or lower abdomen. Digestive Issues Problems like indigestion, constipation, or diarrhea. Back Pain Lower back pain or discomfort. Nausea and Vomiting Feeling nauseous or actual vomiting. Irregular Appetite Changes in hunger levels, either increase or decrease. Fatigue General feeling of tiredness or lack of energy. Bloating Swelling or feeling of fullness in the abdominal area. Urinary Problems Issues like frequent urination or difficulty in urinating. Other than physical symptoms, you might also experience other side effects, like pain and discomfort, nausea and vomiting in case of obstruction, cosmetic problems, functional limitations, diarrhea, constipation and severe stomach ache, loss of appetite, painful periods for women, etc. How to check navel displacement There are some ways you can check if you have navel displacement. Some methods include Simple clinical examination by inspection, Palpation, and Examination for tenderness/inflammation at the umbilicus. Navel displacement causes Causes can range from weak abdominal muscles to pregnancy, obesity, or infection. Navel displacement can be caused by various factors like Weak abdominal muscles Umbilical sinus or fistula, Divarication of rectus, Pregnancy and childbirth, Obesity or Sudden weight gain Infection or inflammation. Improper lifting Genetic predisposition Strain on the abdominal wall Navel displacement treatment >Treatments include non-surgical options like Ayurvedic remedies, chiropractic care, physical therapy, and home remedies >Surgical options like laparoscopic or open surgery may be necessary in severe cases. In order to cure naval displacement permanently You can undergo some medical and non-medical treatments to recover from navel displacements. Here are some of them. The first few remedies are help to cure navel displacement at home that you can follow yourself. If they don’t work, you can visit a laparoscopic surgeon and undergo medical treatments. Non-Surgical Treatment 1. Ayurvedic TreatmentsHerbal Remedies: Ayurvedic practitioners often recommend herbal concoctions like triphala churna, ginger, and ajwain to improve digestion and alleviate symptoms. Abdominal Massage: Gentle massage with warm sesame oil around the navel area can help reposition the navel. This technique should be performed by a trained practitioner. Yoga and Pranayama: Specific yoga postures and breathing exercises, such as Pawanmuktasana, Bhujangasana, and Nadi Shodhana Pranayama, can strengthen abdominal muscles and help realign the navel. 2. Chiropractic CareChiropractors can perform adjustments to the spine and pelvic area to correct misalignments that may be causing navel displacement. These adjustments can help restore balance and improve overall body function. 3. Physical Therapy Core StrengtheningExercises: Engaging in exercises that strengthen the core muscles, such as planks, bridges, and leg raises, can help stabilize the abdominal region and prevent further displacement.Manual Therapy: Physical therapists may use hands-on techniques to manipulate the abdominal muscles and fascia, helping to reposition the navel. 4. Home Remedies Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the abdomen can relax the muscles and facilitate the natural repositioning of the navel. Lie on Your Back: Lying flat on your back with a pillow under your knees for a few minutes daily can help relax the abdominal muscles and support the navel’s return to its natural position. Hydration: Drinking plenty of water and staying hydrated can improve digestion and reduce symptoms associated with navel displacement. 5. Dietary Adjustments High-Fiber Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fiber can promote regular bowel movements and reduce digestive issues related to navel displacement. Avoid Heavy Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can ease digestive strain and help maintain abdominal muscle tone. 6. Acupuncture and Acupressure Acupuncture : This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to balance energy flow and promote healing. Acupressure : Applying pressure to specific points around the navel can stimulate blood flow and support the navel’s return to its proper position. Surgical Options for Navel Displacement Laparoscopic Surgery: During laparoscopic surgery, a surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen. A laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera and light) is inserted through one of the incisions, providing a clear view of the abdominal cavity on a monitor. Special surgical instruments are inserted through other small incisions to perform the necessary corrections. Open Surgery : During open surgery, the surgeon makes a larger incision in the abdominal wall to directly access the displaced navel and surrounding structures. The navel is repositioned, and any necessary repairs to the abdominal muscles or fascia are made. The incision is then closed with sutures or staples. Conclusion Navel displacement can be caused due to various issues. Though it seems to be a serious issue, it can be treated by following some home remedies or medical treatments. If you suspect you have symptoms that are relevant to a navel displacement, it is better not to delay and seek medical intervention and get it treated immediately. Contact Form Demo NameEmailYour MessageSubmit Dr. K. Amilthan MBBS., MS., FMAS., FALS. Heal Your Hernia Now: 20+ Years of Experience 1,000+ Surgeries Your Journey to Wellness Begins with us. Book Appointment
Difference Between Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are advanced surgical methods that use little to no incisions respectively to carry out surgeries. Laparoscopy is often associated with the treatment of issues in the peritoneal region (the abdominal and pelvic region) and hysteroscopy for ailments in the uterine cavity. Yet both laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are used to diagnose and treat gynecological problems. Ailments such as pelvic pain, endometriosis, ectopic pregnancy, etc. can be treated using both laparoscopy and hysteroscopy. The Key Differences Between Laparoscopy And Hysteroscopy Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are minimally invasive surgical procedures. Though both deal with ailments in the peritoneal and uterine cavity there are key differences between the purpose of these surgical procedures. Laparoscopy Hysteroscopy Views the outsides of the organs in the peritoneal cavity. Helps view the insides of the uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix, and ovaries. Diagnoses and operates on organs inside the peritoneal cavity. Diagnoses and operates on female reproductive organs. Treats both infertility issues and ailments of the organs in the peritoneal cavity. Treats infertility-related issues. Employed to diagnose symptoms of ailments in the abdomen and pelvis. Employed to identify the cause of infertility, abnormal uterine bleeding, continuous miscarriages, etc. Minor surgeries are often outpatient surgeries. Major surgeries would require a shorter period of hospitalization. Often an outpatient surgery. Carbon dioxide gas is let into the peritoneal cavity to have a better view of the insides. Saline fluid or carbon dioxide gas is let into the uterine cavity to expand it and have a better view of the insides. Laparoscope is primarily used. A hysteroscope is used. Small incisions are made on the abdomen. No incisions are needed to view the uterine cavity. A laparoscope and other surgical instruments are inserted through the incisions made. A hysteroscope and other surgical instruments are inserted through the vagina and the cervix to view the uterine cavity. Uterine adhesions, ectopic pregnancies, tubal cannulation, and so on are treated using laparoscopy. Fibroids, polyps, and scars in the uterus are treated using hysteroscopy. What Surgeries are Performed Laparoscopically? Laparoscopy is used for surgeries such as: Appendectomy (Removal of the appendix) Cholecystectomy (Removal of gallbladder) Hysterectomy (Removal of womb or uterus) Myomectomy (Removal of leiomyomas or uterine fibroids) Cystectomy (Removal of cysts from the ovary) Oophorectomy (Removal of cysts along with the ovary) Salpingostomy and salpingectomy (Treat ectopic pregnancies) Herniorrhaphy (Removal of hernia) Vagotomy (Cutting off the branch of the vagus nerve to the stomach) Antrectomy or distal gastrectomy (Removal of the lower part of the stomach) Bariatric or metabolic surgery (Weight loss surgery) When do Surgeons Choose Hysteroscopy? Surgeons choose hysteroscopy to treat issues related to the uterus and infertility. Some common issues that surgeons address using hysteroscopy include: Miscarriages Opening of blocked tubes (Tubal cannulation) Menometrorrhagia (Irregular menstrual bleeding) Diagnosis of the uterus Removal of the uterus (due to cancer, adenomyosis and endometriosis) Removal of intrauterine adhesions Removal of septate uterus Myomectomy (Removal of fibroids) Polypectomy (Removal of polyps) Is Laparoscopy a Common Surgical Method? Laparoscopy is a common surgical method employed today. Owing to the fewer post-surgical complications it entails laparoscopy is widely chosen over laparotomy. Surgeons also prescribe laparoscopy to diagnose and treat minor issues in the peritoneal cavity. Laparoscopy has become more advanced with state-of-the-art equipment and improved surgical methods. How Common is Hysteroscopy? Hysteroscopy is one of the most common surgeries done among women. It is generally safe. You can avoid the risks of insomnia, blood loss, mood swings, and other side effects of hysteroscopy by following the mandated prescriptions of the surgeon and by leading a healthy lifestyle. Cancer in the ovaries, uterus, or cervix can be best treated only through hysteroscopy. Advantages of Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy Advantages of Laparoscopy Advantages of Hysteroscopy Makes smaller inciosns. Makes no incisions. The best alternative for laparotomy in case of minor surgeries. Crucial in treating uterine cancer and septate uterus. Treats issues in the pelvic region and the abdominal cavity. Treats infertility-causing issues in the uterine region. Little blood loss. Little to no blood loss. Lesser pain compared to other surgeries. Causes less pain. Hospitalization is not required unless it is a major surgery. Hospitalization is not required most of the time. Shorter operation time. Short surgical time. The recovery rate is quicker. Faster surgery recovery time. Less post-surgery complications. Following physician’s prescriptions reduces post-surgery complications. Incisions do not cause bigger scars. No scarring due to no incisions. Complications of Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy Complications of Laparoscopy Complications of Hysteroscopy Discomfort after surgery in the peritoneal cavity. Discomfort in the uterine cavity after surgery. Scaring of the incisions. Possible scarring of the vaginal tract. Possible perforation of the abdominal wall during surgery. Possible perforation of the uterine wall during surgery. Possible injury to adjacent organs, blood vessels, and nerves. Possible injury to adjacent organs, blood vessels, and nerves. Discomfort due to carbon dioxide gas introduced in the cavity. Discomfort due to saline liquid or carbon dioxide gan introduced in the cavity for operation. Chances of infection in the operated area. Chances of infection in the operated area. Recovery Time for Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy Laparoscopy Hysteroscopy Minor surgeries do not require hospitalization. Hospitalization is not required most of the time. Can resume work within 48 hours. Can resume work within 48 hours. The effects of anesthesia after surgery do not prolong for a long time. The effects of anesthesia after surgery do not prolong for a long time. The discomfort of carbon dioxide gas let into the peritoneal cavity during surgery also wears off sooner. Discomfort due to saline fluid or carbon dioxide gas let into the uterine cavity does not prolong for a longer period Conclusion Both laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are helpful in gynecology-related surgeries. Using laparoscopy or hysteroscopy to address the prevailing ailment is up to the discretion of the surgeon. Just make sure to keep both your body and mind healthy and ready to approach the surgery. Also, weigh the pros and cons of each surgery before opting for one. To know more about the best choice of surgery for
Umbilical vs Ventral hernia
A hernia is a protrusion that most often contains omentum or parts of the intestine. Hernias can cause a lot of pain. But some may go unnoticed for years. Hernias are operated most of the time to prevent adverse scenarios. Umbilical and ventral hernias are hernias that occur in front of the abdomen. An umbilical hernia is also a ventral hernia, as ventral hernias include all the hernias that occur in the anterior region of the abdomen. Thus, a ventral hernia includes umbilical, paraumbilical, epigastric, and incisional hernias. Key Differences Between Umbilical and Ventral Hernia UMBILICAL HERNIA VENTRAL HERNIA A specific term denoting the hernia that occurs at the weak spot of the navel region or belly button. A generic term indicating all hernias that occur on the abdominal front. Occurs in infants, especially premature babies, and in adults. Occurs mostly in adults. Contents of hernia push through the weak spot in the navel or belly button area. Hernia pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. At times would close over time in infants without being operated upon. It can be mild and persist for years with no requirement for surgery. Can be identified through any soft swelling near the belly button. Identified through abnormal swelling in any part of the abdomen. Usually creates no pain in infants. Adults can feel discomfort. Sharp pain, vomiting, and constipation would be associated. Would require surgery if discomfort persists. It would require surgeries most of the time. Is congenital in infants. Obesity, heavy lifting, long-standing coughs, etc also cause it. Caused due to heavy lifting, pregnancy, obesity, abdominal injury, weakened surgical incision covering, and so on. The paraumbilical hernia is an indirect umbilical hernia. Includes umbilical, incisional, inguinal, and other abdomen anterior-appearing hernias. Symptoms of Umbilical and Ventral Hernia The symptoms of both umbilical and ventral hernia are more or less the same. Hernias are usually bulges that are either reducible or irreducible. Reducible hernias are those that can be pushed back inside through the opening of the abdominal wall. Irreducible hernias are those that have become obstructed or strangulated. Obstructed hernias mean that a part of the intestine has got trapped inside the hernia. This will block gas or motion, resulting in severe pain and vomiting. The abdomen may also begin to swell. Strangulated hernias indicate the blocked blood supply to the parts of the body trapped inside the hernia. Cut off blood supply to the intestine or omentum incarcerated inside the hernia can result in tissue death. Blood supply can be restored through immediate surgery. Obstructed and strangulated hernias call for urgent surgical repair. They may turn fatal. UMBILICAL HERNIA VENTRAL HERNIA The bulge becomes discolored. The bulge becomes visible while bending, squatting, or straining oneself physically. Painless in infants most of the time. Causes little to no pain during the early stages. Can get painful around the protrusion area over time. Can cause discomfort in the navel region. Causes discomfort while overexerting. Can cause constipation. Causes constipation with thin stools. Associated with fever, vomiting, tenderness, and pain in the affected area. Associated with nausea, vomiting, and fever due to pain. Causes of Umbilical and Ventral Hernia An umbilical hernia can be congenital. A ventral hernia on the hand is caused only in adults. Causes of Umbilical Hernia Umbilical hernias are caused by: Unclosed abdominal walls during birth Obesity Repeat pregnancies Chronic constipation pressurizing the abdomen Heavy liftingStrainful activities or exercises Excessive abdominal fluid (ascites) Causes of Ventral Hernia Ventral hernias are caused by: Heavy lifting Physical overexertion Obesity Pregnancy Diabetes Long-term coughing Abdominal injury Weakened incision closures Treatment for Umbilical and Ventral Hernias Umbilical and ventral hernias can be easily treated nowadays owing to the advancements in the medical field. Unless the hernia is strangulated or obstructed the hernia repair is executed as a planned procedure. Hernias can operated either through open surgery or through minimally invasive procedures. The size, number, and degree of severity are considered before choosing the surgery type. Treatment for Umbilical Hernia An umbilical hernia is not repaired in infants as there are no possibilities for intestines to get strangulated in them. If the situation persists beyond three years of age in a child, the hernia is suggested to be repaired. Umbilical hernias in adults are mostly advised to be repaired as they can cause severe pain over time. Based on the severity and urgency the kind of surgery is chosen. It can be repaired through open, laparoscopic, or robotic surgery. Treatment for Ventral Hernia Ventral hernia is normally advised to be repaired through surgery. Laparoscopic, robotic, and open surgery facilities are available for ventral hernia treatment. The surgeon would prescribe the best mode of repair based on the severity and necessity of the hernia. Recovery Time for Umbilical and Ventral Hernias With advanced surgical procedures, hernia repair does not require a longer hospitalization period. The recovery period is also quicker. Patients who had undergone umbilical or ventral hernia procedures would require a resting period of two weeks. Works can be resumed after four to five weeks. Yet it is best to not lift heavy objects or be involved in strenuous activities for at least two months. The recovery period ultimately depends on the health status and medical history of the patients as well. Conclusion Umbilical and ventral hernias are commonly occurring hernias and there is no need to worry about it. There are numerous advanced facilities available to treat them nowadays. Visit a nearby hospital to consult a hernia specialist regarding any symptoms you find related to hernia. Follow the physician’s prescriptions and have a healthy recovery. To clear your queries on umbilical and ventral hernias contact a hernia specialist. Contact Form Demo NameEmailYour MessageSubmit Dr. K. Amilthan MBBS., MS., FMAS., FALS. Heal Your Hernia Now: 20+ Years of Experience 1,000+ Surgeries Your Journey to Wellness Begins with us. Book Appointment Edit Template FAQ’s 1) Is an umbilical hernia also a ventral hernia? Yes, an umbilical hernia is also a ventral hernia.
Paraesophageal Hernia Symptoms and Treatment
Paraesophageal hernia occurs in the esophageal hiatus region of the body. The esophageal hiatus is an opening on the diaphragm that separates the chest from the abdominal region. When a paraesophageal hernia occurs, the abdominal and chest cavity organs encounter discomfort. These discomforts and pain in the chest and abdominal region are primary signs of paraesophageal hernia. Hernias require surgical intervention most of the time. This is the same with paraesophageal hernia as well. Your hernia specialist will prescribe the kind of treatment based on the size, location, and severity of the paraesophageal hernia. Upgraded and minimally invasive procedures are available to treat paraesophageal hiatal hernia with little to no blood loss and a faster recovery rate. Symptoms of Paraesophageal Hernia Paraesophageal hernia causes disturbance mainly in the digestive tract and the chest area. Some paraesophageal hernia symptoms include: Severe Chest Pain: When the contents of the stomach move up into the chest cavity it may press against the chest organs resulting in severe chest pain. Shortness of Breath: If the hernia presses against the lungs it can result in shortness of breath. Difficulty in Swallowing: With increasing size of the hernia the act of swallowing may also turn difficult. Nausea and Vomiting: With the food getting trapped in the digestive tract and difficulty in digestion nausea and vomiting can occur. Stomach Pain: With the movement of the stomach and its contents the result of stomach pain occurs. Indigestion: With all the twisting and squeezing and the movement of stomach acid the process of indigestion may become difficult. Bloating and an increase in an uncomfortable level of gas in the abdominal region may also occur. Gastric Acid Reflux: Due to the movement of the stomach contents the acid in the stomach gets transported back and forth into the esophagus irritating the esophageal lining. This results in severe heartburn. This symptom is also called Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Gastric Volvulus: Gastric volvulus refers to the rotation of the stomach. When the stomach ascends next to the esophagus the stomach may get into an upside position causing severe pain, retching, and so on. Ulcers: When the mucosal lining of the esophagus gets frequent acid reflux and lacks enough blood supply due to the constrictions of the hernia ulcers can appear at the neck of the hernia. This is called Cameron’s erosions and can cause severe irritation in the esophageal region. Complications of Paraesophageal Hernia Paraesophageal hernia may be less common but it is a more serious one. It needs to be treated at the right time to prevent strangulation or incarceration. Some paraesophageal hernias exhibit no symptoms at all. Such hernias are also to be observed and consulted for the requirement of surgery or not. Complications of paraesophageal hernia include: Strangulation: Also called ischemia it is a condition in which the blood flow to the tissues of the organs gets cut off due to constriction of the hernia. Incarceration: The herniated organs get trapped and squeezed leading to strangulation. Bleeding: Cameron’s erosions cause ulcers that bleed and may lead to anemia. Gastric Volvulus: The stomach gets twisted causing difficulty in swallowing, retching, and pain. Breathing Trouble: Large-size hernia disrupt the expansion of lugs resulting in shortness of breath. When these complications arise it is advisable to get your paraesophageal hernia immediately treated. Treatments for Paraesophageal Hernia When the paraesophageal hernia begins to show symptoms there is a possibility of the hernia turning into a strangulated or incarcerated hernia. Strangulated and incarcerated hernia can turn fatal and require immediate repair. Non-surgical Treatment The side effects of paraesophageal hernia such as heartburn, nausea, etc. can be treated without surgery through modified lifestyle practices, an appropriate diet like the pre-op diet for hiatal hernia surgery, and so on. However, hiatal hernia repair without surgery is not a complete possibility. Surgical Treatment Symptomatic paraesophageal hernia requires surgical intervention. If you show signs of bleeding from the esophageal region, gastric volvulus, breathing trouble, strangulated or incarcerated hernia quickly undergo a hernia surgery. Laparoscopic surgery is widely employed to treat paraesophageal hernia. It is minimally invasive and operates through the abdominal region itself without disturbing the chest portion. There are certain tests done before hiatal surgery such as barium swallow, esophageal manometry and so on which you will be asked to undertake. Based on the prescribed physical examination your hernia specialist will assess the location, size, and severity of your paraesophageal hernia and prescribe the appropriate surgical procedure. The surgical options available to treat paraesophageal hernia include: Laparoscopic surgery Robotic surgery Open surgery During the surgery, the herniated organs are eased down through the hiatus on the diaphragm to their original position, and the hiatus is closed to prevent future hernia. Or else, the top of the stomach is wrapped around the lower part of the esophagus through stitching. Causes of Paraesophageal Hernia The possible reasons for the occurrence of paraesophageal hernia include: Large hiatus at birth Obesity Lifting heavy objects Repeated vomiting Chronic coughs Strained bowel movements Wear and tear of the hiatus with age (usually above 50 years of age) Blunt trauma or injury (eg: Seatbelt pressure on the hiatal region during a road accident) Conclusion Paraesophageal hernia may be painful and wearisome but it will go away with appropriate treatment in due time. There are various surgical procedures available to treat paraesophageal hiatal hernia. So contact a hernia specialist as soon as you encounter any of the above-listed symptoms and complications. To know more details about paraesophageal hiatal hernia symptoms and treatment contact a hernia specialist. Contact Form Demo NameEmailYour MessageSubmit Dr. K. Amilthan MBBS., MS., FMAS., FALS. Heal Your Hernia Now: 20+ Years of Experience 1,000+ Surgeries Your Journey to Wellness Begins with us. Book Appointment Edit Template FAQ’s 1) Will a paraesophageal hernia go away? Yes, a paraesophageal hernia will go away if treated in due time. Make sure not to leave the hernia to turn strangulated or incarcerated as it can cause mortality. 2) How do you treat a paraesophageal hernia? The treatment for a paraesophageal hernia is based on its size and severity. Your hernia specialist will decide upon the kind of treatment
The Key Differences of Femoral and Inguinal Hernias
Femoral and inguinal hernia are groin hernia as they appear in the groin area of the body, especially in the inner thigh region. The major difference between femoral and inguinal hernia is that the femoral hernia protrudes through the femoral canal and the inguinal hernia through the inguinal canal in the groin. Both hernias occur due to the contents in the abdomen, primarily the omentum and parts of the bowels, penetrating through a weak spot in the abdominal wall to the groin area. Difference Between Femoral and Inguinal Hernia FEMORAL HERNIA INGUINAL HERNIA A hernia that protrudes through the femoral canal in the groin. A hernia that protrudes through the inguinal canal in the groin. Occurs mostly in females. Occurs mostly in males. Contents of the hernia push through the weak spot in the abdominal muscle into the femoral canal. Contents of the hernia push through the weak spot in the abdominal muscle into the inguinal canal. Have a higher risk of strangulation. The risk of strangulation is lesser than a femoral hernia. Identified through a soft swelling below the inguinal ligament. Identified through a bulge in the groin. Causes enlarged scrotum in men. Most femoral hernias are asymptomatic. Causes considerable discomfort. Requires surgery most of the time as it is highly prone to incarceration. Bearable without surgery if discomfort does not prolong. Caused by pregnancy, weight gain, muscle strain, etc. Is congenital in children. Caused by increasing age, chronic cough, constipation, heavy lifting, obesity, etc. The hernia sac consists of the omentum mostly. The hernia sac consists of bowel parts. Symptoms of Femoral and Inguinal Hernia The symptoms of both femoral and inguinal hernia are more or less the same. They are either reducible or irreducible also. Reducible hernias can be pushed back through the abdominal wall whereas irreducible hernias cannot be. Irreducible hernias have higher risks of being obstructed or strangulated. A femoral hernia becomes visible as a bulge during coughing or straining. It is asymptomatic most of the time but can turn painful if it becomes obstructed or strangulated. An inguinal hernia appears as a bulge on the side of the pubic bone and causes a burning sensation or pain in the groin region. It can cause pain and swelling around the testicle region for men. An inguinal hernia can also descend through the scrotum and make it enlarged. It also causes huge pain while standing for a long time. Causes of Femoral and Inguinal Hernia Femoral and inguinal hernia have similar reasons for occurrence. Only that women are more prone to femoral hernia and men are more prone to inguinal hernia. Causes of Femoral Hernia Femoral hernias are caused by: Obesity Multiple pregnancies Chronic constipation Heavy lifting Strenuous activities or exercises Causes of Inguinal Hernia Inguinal hernias are caused by: Heavy lifting Strain of the abdominal muscles Obesity Pregnancy Chronic coughing Treatment for Femoral and Inguinal Hernia Femoral and inguinal hernia can be operated upon if they cause much pain and discomfort. Also, to prevent obstruction and strangulation it is wiser to operate on the hernia in due time. There are advanced surgical methods available to repair these hernias. Some include: Open surgery Laparoscopic surgery or keyhole surgery Robotic surgery Treatments for Femoral Hernia Smaller hernias may not require surgical repair. However, large and discomforting femoral hernia can be operated on through either open or laparoscopic surgery based on the severity of the hernia and the urgency to repair it. Treatments for Inguinal Hernia Inguinal hernia can be repaired through open and laparoscopic surgeries. There are three kinds of hernia repair: Herniotomy: Hernial sac is removed. Herniorrhaphy: Hernial sac is removed alongside repairing the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. Hernioplasty: a synthetic mesh is used to reinforce the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. Recovery Time for Femoral and Inguinal Hernia You can recover from femoral and inguinal hernia repair within a few weeks. The advanced surgical procedures have reduced recovery time and guarantee speedier recovery with minimal infection and pain You may have to avoid driving until you are weaned off painkillers. You can resume work but stay away from lifting heavy weights. Conclusion Femoral and inguinal hernias can be treated easily with the latest surgical procedures available today. So it is not to be worried about. Incorporate a healthy lifestyle by reducing weight that causes straining of the hernia, adopting a healthy diet, and so on. Follow the advice of the hernia specialist and have a healthy and speedy recovery. To clear your queries on femoral and inguinal hernias contact a hernia specialist. Contact Form Demo NameEmailYour MessageSubmit Dr. K. Amilthan MBBS., MS., FMAS., FALS. Heal Your Hernia Now: 20+ Years of Experience 1,000+ Surgeries Your Journey to Wellness Begins with us. Book Appointment Edit Template FAQ’s 1) How can you tell the difference between an inguinal and a femoral hernia? Both inguinal and femoral hernia appear in the groin region with contents of the abdomen forming a bulge of the hernia sac. The femoral hernia appears a bit lower than the inguinal hernia region. The inguinal hernia passes through the inguinal canal and the femoral hernia through the femoral canal. 2) Is femoral the same as inguinal hernia? No, the femoral hernia penetrates through the femoral canal whereas the inguinal hernia passes through the inguinal canal. 3) Is a femoral hernia a type of inguinal hernia? No, a femoral hernia is not a type of inguinal hernia. It is a groin hernia that occurs lower to the inguinal hernia region and through the femoral canal. Dr. Amilthan Dr. Amilthan is a renowned laparoscopic hernia surgeon based in Chennai, with over 20 years of experience in general surgery. He completed his MBBS and MS in General Surgery at Kilpauk Medical College and Government Royapettah Hospital in Chennai. Edit Template All Posts Hernia Blog The Key Differences of Femoral and Inguinal Hernias Femoral and inguinal hernia are groin hernia as they appear in the groin area of the body, especially in the… Read More Clinical Features of Femoral Hernia A femoral hernia, also
Clinical Features of Femoral Hernia
A femoral hernia, also called femorocele, is a type of hernia that occurs in the femoral canal of the human body. The protrusion of the abdomen content through the femoral canal characterizes a femoral hernia. There are upgraded medical technologies available to treat femoral hernias today. So, if you are diagnosed with a femoral hernia, you do not have to worry. Grasp adequate knowledge of femoral hernia and prepare for the treatment without fear. Understanding of Femoral Hernia A femoral hernia occurs when the content of the abdomen slips through a weak spot in the abdominal wall and passes through the femoral canal. The femoral canal is in the inner thigh region parallel to the pubic bone and consists of the femoral artery, veins, and nerves. The content of the femoral hernia consists of the omentum or parts of the bowels. Symptoms of Femoral Hernia If the femoral hernia is small and reducible, it does not cause much pain. You can manage an asymptomatic hernia without treatment. When the femoral hernia is large, it can be highly discomforting and cause pain when you stand for long or lift heavy objects. A large femoral hernia is visible as a bulge on the body’s surface. Symptoms of a severe femoral hernia include Nausea Vomiting Severe abdominal pain Severe groin pain, etc. Causes of Femoral Hernia A femoral hernia is caused by: Pregnancy weight Obesity Weak abdominal wall Chronic constipation Heavy lifting, etc. Femoral Hernia Complications A femoral hernia is not complicated until it turns symptomatic and incarcerated or strangulated. An obstructed or strangulated femoral hernia can turn fatal and call for immediate medical attention. Obstructed Femoral Hernia An obstructed femoral hernia indicates that the content of the hernia is stuck inside the femoral canal and cannot return to its original position. Strangulated Femoral Hernia A strangulated hernia means that the content of the hernia is stuck in the femoral canal and the blood supply is cut. This can cause the death of the tissues in the region and turn fatal. Treatment for Femoral Hernia There are both surgical and non-surgical options available to treat femoral hernia. Surgical Options Surgical options for treating a femoral hernia include: Laparoscopic surgery Open surgery Robotic surgery Laparoscopic and robotic surgery are minimally invasive and widely preferred. Open surgery is preferred in complicated scenarios. In femoral hernia surgery, the contents of the hernia are pushed back to the original position, and the hole is meshed to prevent future hernia. Non-Surgical Options The non-surgical option is available only for the femoral hernia that is small, asymptomatic, and bearable. You would have to follow the advice of the hernia specialist regarding this case on how to take care of a femoral hernia without surgery. Also, take the prescribed medication to ease the possible discomfort of the hernia and prevent the hernia from getting severe. Recovery Time After Femoral Hernia Treatment If minimal invasive techniques are employed to treat the femoral hernia, you can recover within two weeks of surgery. With minimally invasive technology, the recovery period is quicker, with little post-surgical pain as well. Conclusion Women are more prone to femoral hernia than men. Small femoral hernias are asymptomatic most of the time. But when it gets large and the severity of discomfort increases, you may have to consult a hernia specialist and get treated to prevent incarceration or strangulation. To stay carefree from femoral hernia, adopt a healthy lifestyle and diet, exercise, and maintain a healthy BMI (Body Mass Index). You can always undertake a hernia repair if required. To know more about femoral hernia and how to treat it, consult a hernia specialist. Contact Form Demo NameEmailYour MessageSubmit Dr. K. Amilthan MBBS., MS., FMAS., FALS. Heal Your Hernia Now: 20+ Years of Experience 1,000+ Surgeries Your Journey to Wellness Begins with us. Book Appointment Edit Template FAQ’s 1) What is the clinical test for femoral hernia? Ultrasound can help assess the bulge in the groin area if you suspect it to be a femoral hernia. If there are no visible bulges, you can use imaging tests to confirm. 2) What is the characteristic shape of a femoral hernia? A femoral hernia usually has a funnel-shaped neck protruding from the femoral canal. 3) What is the most common site of femoral hernia? The most common site of femoral hernia is the upper part of the inner thigh where the femoral canal lies. Dr. Amilthan Dr. Amilthan is a renowned laparoscopic hernia surgeon based in Chennai, with over 20 years of experience in general surgery. He completed his MBBS and MS in General Surgery at Kilpauk Medical College and Government Royapettah Hospital in Chennai. Edit Template All Posts Hernia Blog Clinical Features of Femoral Hernia A femoral hernia, also called femorocele, is a type of hernia that occurs in the femoral canal of the human… Read More Femoral Hernia in Child Femoral hernias are rare groin hernias and are rarer in children. Femoral hernia in children may occur due to openings… Read More Femoral Hernia in Women Femoral hernias are a type of groin hernia that occurs mostly in women. Femoral hernias are characterized by the abdominal… Read More Load More End of Content.